Symptoms and Treatment of Esophagitis
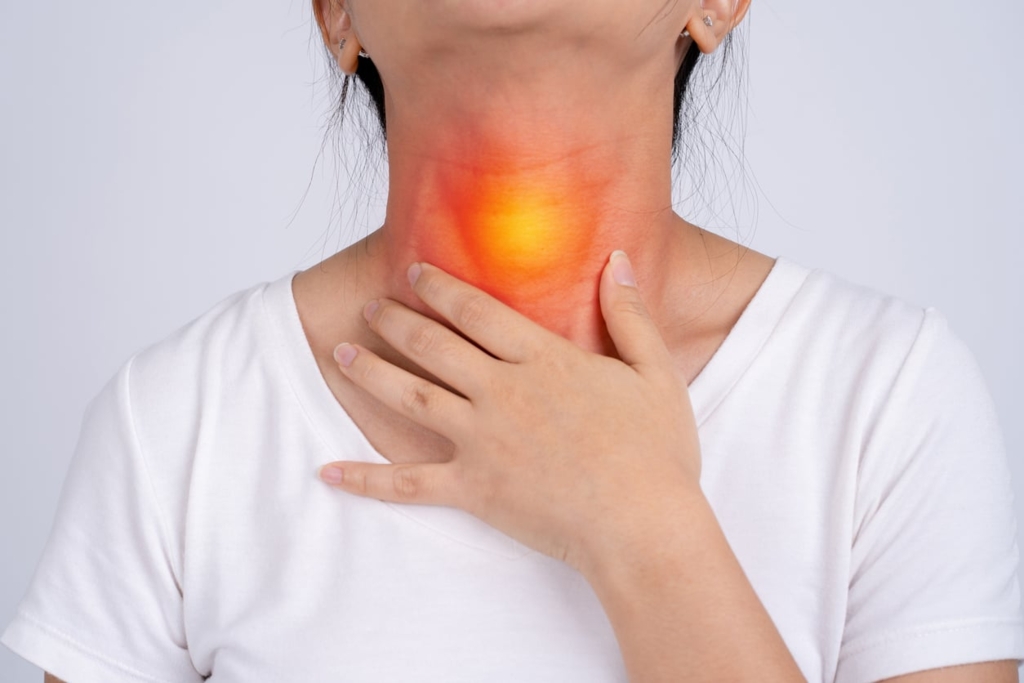
Esophagitis is a condition that affects the esophagus, which is the tube that carries food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach. Esophagitis can cause a variety of symptoms, including chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes of esophagitis, as well as the symptoms and treatment options available.
What Causes Esophagitis?
Esophagitis can be caused by a variety of factors, but the most prevalent is gastroesophageal reflux disease, generally known as GERD. When stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, irritates and inflames the esophagus. Certain medications, such as antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can potentially induce esophagitis (NSAIDs). In addition, the illness can be triggered by hot beverages or extremely spicy foods.
What Are the Symptoms of Esophagitis?
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the throat to the stomach. The most common symptom of esophagitis is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest and throat. Other symptoms include trouble swallowing, pain with swallowing, and chest pain. In severe cases, esophagitis can lead to bleeding in the esophagus or ulcers (sores) in the lining of the esophagus. Esophagitis is usually caused by an infection, although it can also be caused by acid reflux or chemicals. Treatment for esophagitis depends on the cause and may include antibiotics, antacids, or surgery.
What Tests Might Be Done?
Endoscopy is the most common test used to diagnose esophagitis. During this procedure, a long, flexible tube with a light and camera attached is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus. This allows the doctor to carefully examine the inside of the esophagus for signs of irritation or damage. Sometimes, a small sample of tissue (biopsy) will be taken during endoscopy for further testing. Other tests that may be used to diagnose esophagitis include x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and upper GI series (a type of x-ray that looks at the upper gastrointestinal tract). These tests can help to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of esophagitis.
What Are the Treatments for Acid Reflux and Esophagitis?
Both conditions can be treated with medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery. Medications for acid reflux and esophagitis include antacids, proton pump inhibitors, histamine blockers, and foam barriers. Lifestyle changes that can help to reduce symptoms include avoiding trigger foods, quitting smoking, eating smaller meals, and elevating the head of the bed. Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases of acid reflux or esophagitis that do not respond to other treatment options. With proper treatment, most people with acid reflux or esophagitis can find relief from their symptoms.
What Are the Complications from Esophagitis?
While most cases of esophagitis are mild and resolve on their own, some can lead to more serious complications. These include ulcers in the esophagus, bleeding, and difficulty swallowing. In rare cases, esophagitis can also lead to a condition called Barrett's esophagus, which increases the risk for esophageal cancer. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential complications of esophagitis and to seek medical treatment if symptoms persist.